How green is heating with a heat pump?
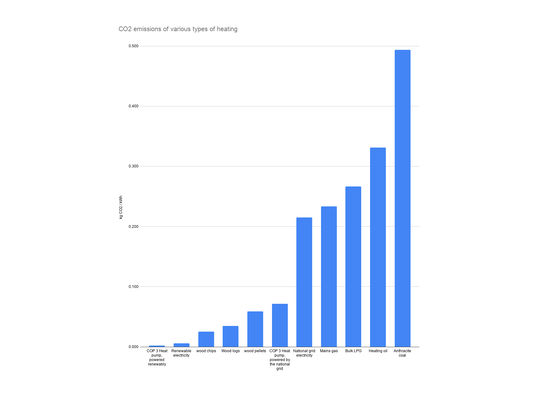
Run off the UK National Grid in 2024 a heat pump would have resulted in around 80% lower CO2 emissions than heating with a gas boiler, and nearly 90% less than oil heating systems.
Heat pumps are powered by electricity, so just how sustainable a heat pump heating system is very much depends on where that electricity is coming from. But even just plugged into the UK's national grid a heat pump produces a lot less CO2 than gas or oil heating.
Plugged into a truly renewable electricity supply and heat pumps emit over 100 times less CO2 than gas, and over 150 times less than oil heating!
So if you are installing a heat pump then definitely also consider switching to a 100% renewable electricity supply.
The emission factors here are from SAP 2019, National Grid ESO, and Carbonbrief. The heat pump COP (efficiency) assumed for the calculation is 3. So for every kWh of electricity this heat pump would, on average, provide 3 kWh of heat.
You can also see there's a distinctly renewable end to the graph - heat pumps and biomass beat gas and oil hands down when it comes to impact on climate change. Below are the figures that the graph is drawn from, as well as the sources of information used.
| Heating Type | kg CO2/kWh | |
| COP 3 Heat pump, powered renewably | 0.002 | |
| Renewable electricity | 0.006 | https://www.carbonbrief.org/solar-wind-nuclear-amazingly-low-carbon-footprints |
| Wood chips | 0.026 | From SAP 2019 |
| Wood logs | 0.035 | From SAP 2019 |
| Wood pellets | 0.059 | From SAP 2019 |
| COP 3 Heat pump, powered by the national grid | 0.041 | |
| National grid electricity | 0.124 | National Grid ESO, UK grid carbon intensity for 2024 |
| Mains gas | 0.233 | From SAP 2019 |
| Bulk LPG | 0.267 | From SAP 2019 |
| Heating oil | 0.331 | From SAP 2019 |
| Anthracite coal | 0.494 | From SAP 2019 |